Reverse osmosis systems remove dissolved salts, heavy metals, chemicals, and microorganisms from water. In this article, we will explore what do reverse osmosis systems remove from water, helping you understand how they ensure clean water.
Key Takeaways
- Reverse osmosis systems effectively remove a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, microorganisms, and organic compounds, ensuring safe drinking water.
- While reverse osmosis provides significant health benefits and improves water taste and odor, it may also strip essential minerals, necessitating remineralization for optimal health benefits.
- Understanding the limitations of reverse osmosis, such as the inability to remove certain dissolved gases and specific contaminants, is crucial for comprehensive water purification and safety.
Understanding Reverse Osmosis
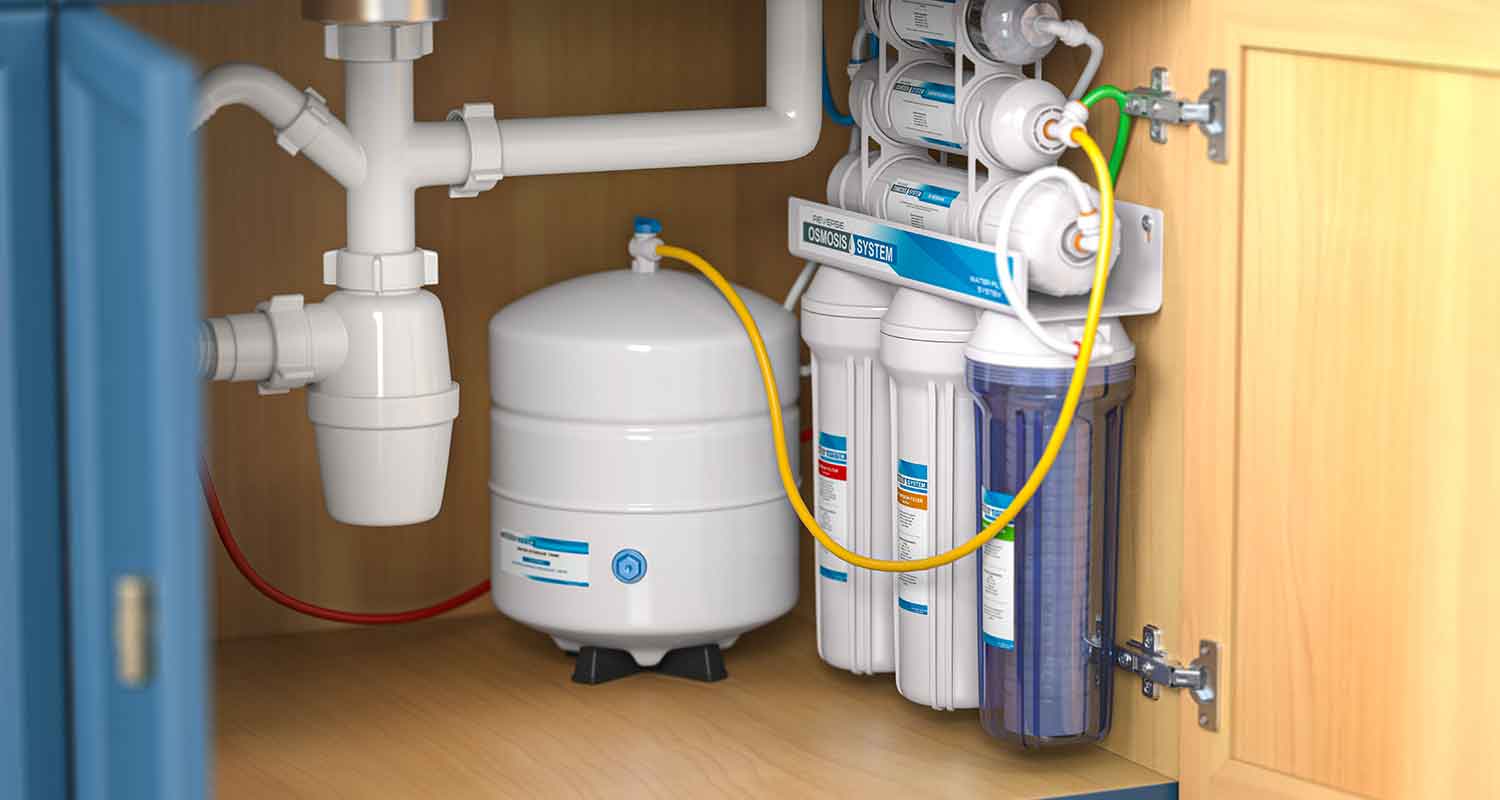
Reverse osmosis is an effective method of water purification that removes contaminants using a semi-permeable membrane under pressure. This method has become a cornerstone of modern water filtration systems, providing an efficient way to ensure the ro water we consume is clean and safe with a reverse osmosis membrane, reverse osmosis filters, and reverse osmosis ro.
The core of any reverse osmosis system is its RO membrane, which filters out impurities. As water moves through this membrane, contaminants are left behind, producing purified water suitable for drinking and other uses. This process improves water quality and ensures the water is free from harmful substances.
The Science Behind Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis uses applied pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane, effectively filtering out contaminants. This pressure, known as osmotic pressure, helps the process overcome osmotic pressure and the natural tendency of water to flow from low solute concentration to high solute concentration areas. Understanding how osmosis works is essential for grasping the principles behind reverse osmosis.
The membrane surface is designed to let only water molecules pass through while blocking larger contaminants such as salts and bacteria. This selective permeability is what makes reverse osmosis so effective at purifying water. The movement of water and retention of contaminants are governed by principles of size exclusion and steric hindrance, ensuring that only pure water molecules make it through the semipermeable membrane surfaces filtration process.
Understanding the science behind reverse osmosis highlights the technology’s precision and effectiveness in providing high-quality drinking water. Leveraging these principles, reverse osmosis systems offer a reliable solution for ensuring safe, clean water.
Contaminants Removed by Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis systems are known for their ability to remove a wide range of contaminants from water, making it safe for consumption. These systems effectively eliminate:
- dissolved salts
- impurities
- minerals
- chemicals
- pollutants ensuring high-quality purified water.
Reverse osmosis systems have impressive rejection rates, removing 95% to 99% of various impurities in the feed water. We will explore what reverse osmosis can remove, including:
- Inorganic compounds
- Organic compounds
- Microorganisms
- Particulates and sediments.
Inorganic Compounds
Reverse osmosis systems excel at reverse osmosis remove inorganic compounds, including dissolved salts and heavy metals, from water. They can eliminate 95-99% of dissolved salts, ensuring the water is free from these potentially harmful substances.
Reverse osmosis can also remove up to 98% of toxic heavy metals, including:
- lead
- arsenic
- chromium
- cadmium This effectively reduces exposure to these dangerous contaminants. This high level of removal ensures that the water is not only safe but also healthier to consume.
Organic Compounds
Reverse osmosis systems can effectively filter out common contaminants, including pesticides and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These substances often pose significant health risks, and their removal is crucial for ensuring safe drinking water.
While effective against many organic compounds, reverse osmosis does not significantly remove dissolved gases like methane and radon. However, using a carbon filter with activated carbon filters alongside reverse osmosis can enhance the removal of these organic materials, ensuring comprehensive water purification:
- Reverse osmosis alone is effective against many organic compounds.
- It does not significantly remove dissolved gases such as methane and radon.
- Activated carbon filters can be used alongside reverse osmosis.
- This combination enhances the removal of organic materials and dissolved gases.
- Together, they ensure comprehensive water purification.
Microorganisms
Reverse osmosis technology can significantly reduce various microorganisms, including bacteria and viruses. By filtering out these pathogens, reverse osmosis systems reduce the risk of gastrointestinal diseases and other health issues related to contaminated water.
However, reverse osmosis systems do not effectively eliminate all bacteria and viruses; however, reverse osmosis remove bacteria. Additional treatment methods may be needed to ensure complete microbial safety, especially in areas with known contamination issues.
Particulates and Sediments
Reverse osmosis systems are also effective at removing large particles and sediments from water. This removal is vital for producing clear, high-quality water free from visible impurities.
Capturing these particulates and sediments, reverse osmosis systems with a sediment filter enhance water clarity and quality. This makes the water more aesthetically pleasing and ensures it is safe and pleasant to drink.
Additional Benefits of Reverse Osmosis Filtration
Besides removing contaminants, reverse osmosis systems offer several additional benefits that contribute to water quality and environmental sustainability. These systems reduce the environmental footprint by lowering the need for single-use plastic, reducing pollution, and decreasing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Efficient water purification through reverse osmosis enhances water quality, significantly impacting health concerns and well-being. We will explore these benefits in more detail, focusing on improved taste and odor, and high purity water health benefits.
Improved Taste and Odor
One immediate benefit of reverse osmosis systems is the significant improvement in water taste and odor. Remove chlorine up to 98%, reverse osmosis systems eliminate the unpleasant taste and smell often associated with tap water.
This improvement in taste and odor makes the water more appealing for drinking and cooking, promoting better hydration and a healthier lifestyle. Removing contaminants that cause bad taste and odor and removing impurities ensures the water is safe and enjoyable to consume.
Health Benefits
Reverse osmosis systems provide significant health benefits by removing harmful contaminants from water, leading to improved health outcomes. Compliance with drinking water quality guidelines is crucial for public health, and reverse osmosis achieves this by reducing exposure to dangerous substances.
However, reverse osmosis can also strip away essential minerals from the water, potentially affecting its mineral content and health benefits. This drawback can be mitigated by employing remineralization techniques to restore beneficial minerals in the water.
Limitations of Reverse Osmosis Systems
Although reverse osmosis systems are highly effective, they do have certain limitations. For example, they may not remove contaminants such as:
- Cryptosporidium
- Giardia
- Hexavalent chromium These contaminants could be present in some water supplies and pose health risks, indicating the need for additional treatment methods.
Scaling can occur in reverse osmosis systems when dissolved inorganic compounds exceed their solubility limits, reducing efficiency. Recognizing these limitations is crucial for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of water purification.
Dissolved Gases
Certain dissolved gases, like carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, are not effectively removed by reverse osmosis systems due to their low molecular weight and lack of ionization. This inability can impact overall water quality, indicating the need for additional treatment methods to address these specific contaminants.
Considering dissolved gases when evaluating reverse osmosis systems is important to ensure comprehensive water purification and safety.
Minerals and Nutrients
Reverse osmosis filtration removes essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium from water, removing minerals that ensure the removal of harmful substances. It also means beneficial minerals are lost, potentially reducing the water’s health benefits.
To counteract this, users can employ remineralization techniques, such as adding mineral drops or using remineralizers, to restore beneficial minerals in the water. This approach helps maintain the water’s health benefits and taste while ensuring it is safe to drink.
Enhancing RO System Performance
Enhancing the performance of reverse osmosis systems is key to achieving high-quality water production. Adequate pressure, typically within the range of 40 to 100 psi, is crucial for ensuring the efficiency of RO membranes and maintaining an optimal flow rate.
Using a booster pump or a permeate pump can significantly improve system performance, especially with high total dissolved solids (TDS). We will explore these methods in more detail, focusing on pre-treatment solutions and regular maintenance.
Pre-treatment Solutions
Pre-treatment is essential to prevent fouling, scaling, and premature failure of RO membranes. Proper pre-treatment protects the membranes from contaminants that could cause fouling and scaling, ensuring the system’s longevity and efficiency.
Techniques like using antiscalants, water softeners, and pre-filters (like Granular Activated Carbon) are essential for effective pre-treatment in the water purification process. These methods help remove silt, chlorine, and other contaminants, extending the system’s life and improving feed water quality with a water filter.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including filter changes and inspections, is necessary to ensure the optimal performance of reverse osmosis systems. Cleaning ro filters and RO membranes 1 to 4 times a year maintains their effectiveness and prevents fouling.
Indicators like pressure drops, increased salt passage, and reduced permeate flow signal the need for membrane cleaning. Using both low and high pH cleaners can effectively remove fouling materials, ensuring the system continues to produce high-quality water.
Choosing the Right RO System for Your Needs
Choosing the right reverse osmosis system involves understanding your specific water quality needs. Conducting a water analysis can help identify the contaminants in your water and guide you in choosing the most suitable system.
It is also important to look for certifications that verify the effectiveness and safety of reverse osmosis systems. Regular maintenance, including timely filter replacements and system sanitization, is essential to maintain the system’s performance.
We will further explore the differences between point-of-use and point-of-entry systems, as well as certification standards.
Point-of-Use vs. Point-of-Entry Systems
Point-of-Entry systems treat water at the main supply line, providing filtered water for the entire household. In contrast, Point-of-Use systems filter water at the point of consumption, such as kitchen sinks, ensuring the water used for drinking and cooking is purified.
Understanding the differences between these systems can help you choose the right one for your needs, ensuring that you have access to clean, safe water fed where it matters most.
Certification and Standards
Certification is essential for ensuring that reverse osmosis systems meet industry standards for safety and performance. Look for certifications like the NSF performance standards and the Water Quality Association Gold Seal, which indicate that the product meets rigorous criteria for water filtration.
Consumers should always check for these certifications to ensure that the RO systems they purchase are both effective and safe, providing peace of mind and assurance of quality.
The Bottom Line
In summary, reverse osmosis systems offer a highly effective solution for removing a wide range of contaminants from water, ensuring safe drinking water. From inorganic compounds and organic substances to microorganisms and particulates, these systems provide comprehensive water purification.
While there are limitations, such as the inability to remove certain dissolved gases and essential minerals, these can be mitigated with additional treatment methods and remineralization. By understanding the science behind reverse osmosis, the benefits, and the limitations, you can make an informed decision about whether this technology is right for you.
Sources:
- https://espwaterproducts.com/pages/what-does-a-reverse-osmosis-system-remove?srsltid=AfmBOoo_fLXmB4wMabCxszj6enbPYZdvtMEvXed1mfmSt7FBCnNN3Hsx
- https://puretecwater.com/resources/the-basics-of-reverse-osmosis/
- https://quench.culligan.com/blog/what-is-reverse-osmosis-and-how-does-it-work/
- https://extensionpubs.unl.edu/publication/g1490/2014/html/view
- https://eaiwater.com/reverse-osmosis-removal-capabilities/