Your Guide To Water Softeners
If you have noticed that your shampoo doesn’t lather very well, there is a film in your bath or shower, or your dishes have spots on them even though you’ve cleaned them, it’s likely that your home is receiving hard water. Hard water can come from both city water and well water, and even city water may still contain minerals that require softening.
Hard water refers to water that has a lot of hardening minerals in it such as calcium and magnesium ions, as well as carbonate, manganese, and calcium. Calcium carbonate is a common cause of scale and buildup in plumbing.
If you have a hard water problem, you can use water softeners to remove the minerals from the water. Hard water can also cause dry skin and affect personal hygiene. By using water softeners, you can stop your pipes from clogging, and you’ll be able to lather up the shampoo in the shower.
It is important to test a water sample for dissolved solids and mineral content, whether your water comes from a municipal water supply or a private well. If you have a water softener unit installed, it should last you for quite a few years, but it will need some maintenance now and then. Hard water can also cause scale buildup on heating elements, reducing the efficiency and lifespan of hot water appliances.
Should I Buy A Water Softener?

Although the minerals found in hard water aren’t harmful towards your health, it can be a nuisance as they create a build up in your plumbing, the appliances that use water, and in your water heater. They can also make washing your clothes, dishes, and showering a harder task.
Throughout America, there are around 85% of homes that suffer from hard water. Water hardness is typically measured in grains per gallon, with one grain being a standard unit used to determine the capacity of water softeners.
Pros of Water Softeners
- Having a water softener installed means you won’t suffer from as much scale
- The chances of your pipes clogging are a lot less likely
- By having less scale, you can save on your water heater’s energy cost
- Scale buildup goes down in appliances that use water
- Soaps and detergents can lather and work a lot better
- There will be a reduction in spotting and staining when washing clothes and dishes
- The lifespan of appliances can increase
- Softening water helps prevent scale buildup and improves water quality throughout the home
- Some water softener systems also provide iron removal, which helps prevent staining and improves water quality
- Properly installed water softeners help maintain consistent water pressure by preventing mineral buildup in pipes
Cons of Water Softeners
- With a sodium-based ion exchange softener, your salt intake can increase
- Salt usage in water softeners can vary depending on water hardness and system size, which may affect maintenance frequency and cost
- Some homeowners are concerned about the impact of water softener regeneration on their septic system, but studies show that, under normal circumstances, it does not negatively affect septic performance or drain field soil percolation
- Softened water is safe to drink, but many people don’t enjoy the taste of it
- The unwanted minerals from your water go to waste
How Water Softeners Work
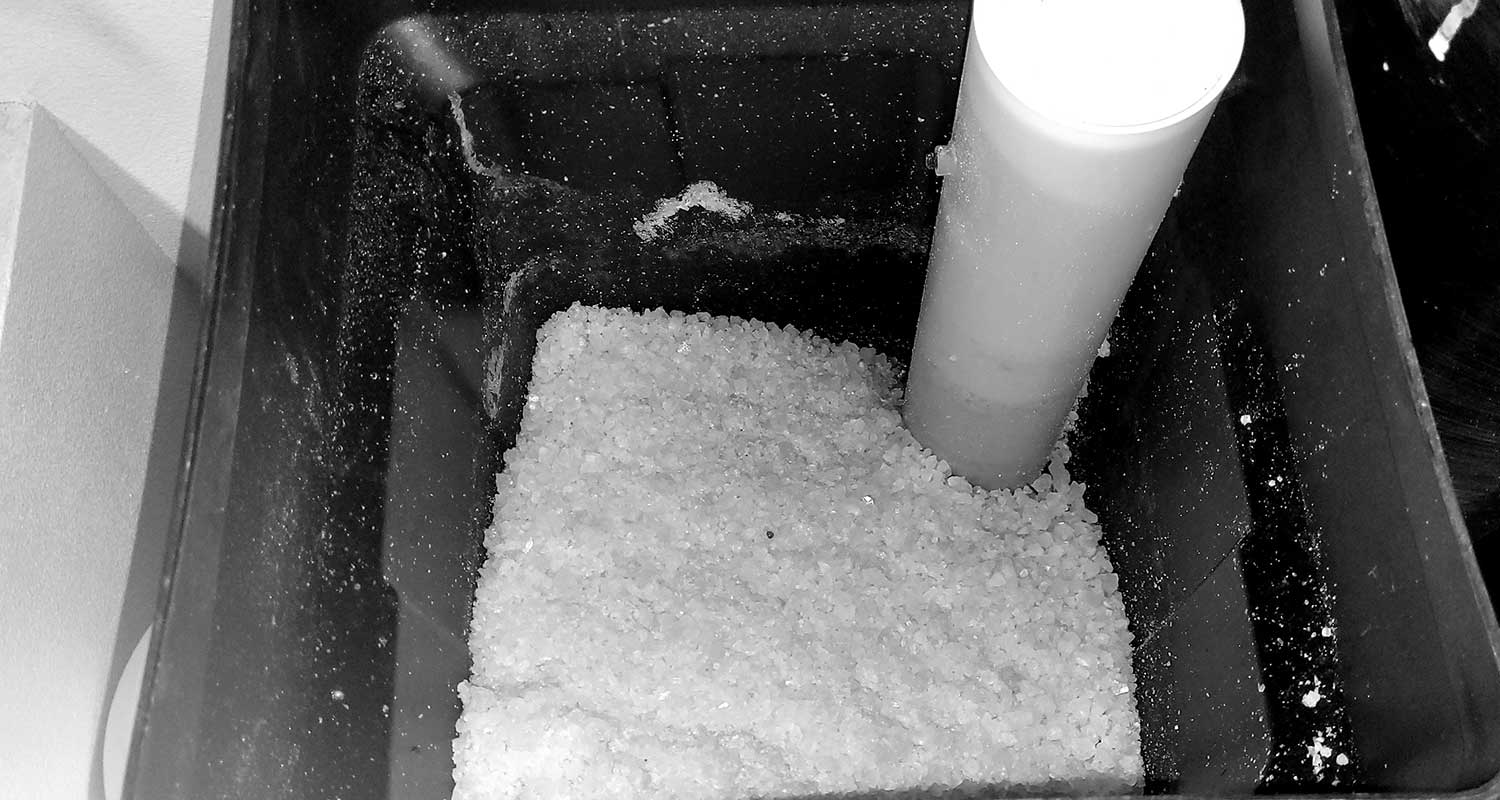
A water softener is designed to tackle water hardness by removing minerals like calcium and magnesium that cause scale and buildup in your plumbing. Most water softeners use a process called ion exchange to soften water. Here’s how it works: as hard water flows into the water softener, it passes through a resin bed filled with tiny resin beads.
These beads are charged with sodium ions. When the hard water comes into contact with the resin beads, the magnesium and calcium ions in the water are swapped out for sodium ions. This exchange effectively removes the hardness minerals, resulting in softened water that flows out to your home.
Over time, the resin bed becomes saturated with magnesium and calcium ions and can no longer soften water efficiently. That’s when the regeneration cycle kicks in.
During regeneration, the water softener flushes the resin beads with a brine solution rich in sodium, which washes away the accumulated minerals and recharges the beads with sodium ions. After this cycle, the water softener is ready to continue providing your home with softened water.
Types of Water Softeners, Including Dual Tank Water Softeners
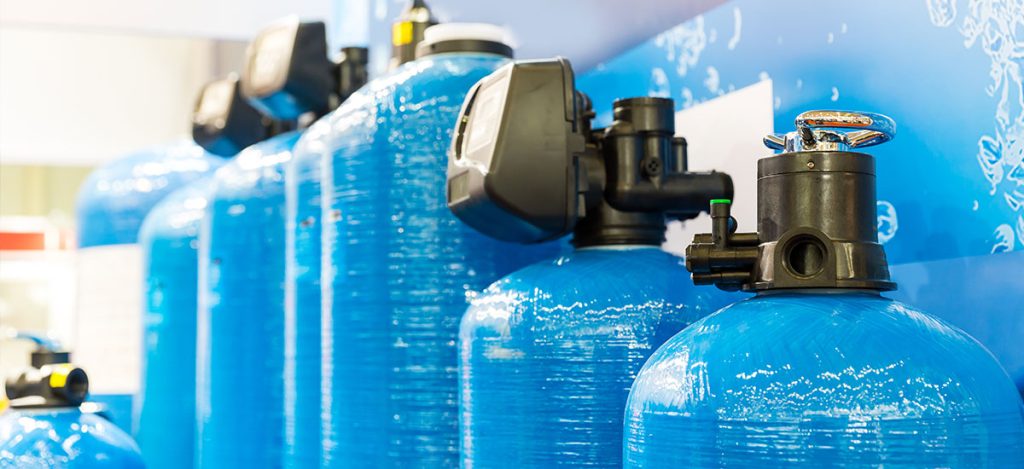

The most common type of water softener is an ion exchange unit, but this isn’t the only kind that is available. There are several types of water softener systems, including salt based systems, salt free systems, and magnetic water softeners. If you are looking to get a water softener unit, you should first know about the types that are on offer.
Sodium-based ion exchange softener – This is a salt based water softener. Before the water enters your household pipes, it will cycle the water through two different tanks: a brine tank and a mineral tank. The mineral tank contains resin beads that facilitate the ion exchange process, where hardness particles such as magnesium and calcium are removed from the incoming water and replaced with sodium ions. During regeneration, the salt from the brine tank flushes the hardness particles off the resin beads, restoring the softener’s effectiveness. Salt based softeners are especially effective for treating well water and high levels of hardness.
Dual tank water softener – A dual tank water softener has two resin tanks, which means softened water can be supplied to your home constantly. A non-dual tank water softener cannot provide you with softened water continuously as it must recharge. It will most likely regenerate over the night, but it can become problematic if you need to use your water while the regeneration cycle is occurring. With a dual tank, while one tank regenerates, the other tank can be utilized.
If you wish to buy a dual tank water softener, you need to think about the space it requires. Depending on what type of dual tank water softener you get, there are different requirements, so you need to consider these before you purchase one.
Sodium-free water softener – Salt-free water softeners, also known as salt free systems, salt free softeners, or salt free water conditioners, are great for those who don’t have much space as they have been specifically designed for tight spaces. Rather than using sodium, this water softener uses a potassium chloride that is a salt substitute. Some salt free systems use template assisted crystallization (TAC) to reduce limescale formation by altering the structure of hard water minerals.
With this type of water softener, the minerals in the hard water aren’t removed; instead, the salt free system changes their structure to prevent scale buildup, making it a de-scaler. Installation is straightforward, as it connects directly to the incoming water supply. While it isn’t as effective as some of the other water softeners at removing minerals, it is still useful for scale prevention.
Magnetic water softener – Magnetic water softeners are compact, space-saving devices that are easy to install, making them suitable for small homes, RVs, or apartments. This water softener is an electrical device that simply clips onto your home’s incoming pipe. A magnetic field is set up, and the electromagnetic properties are changed in some of the minerals.
This means the minerals are repelled by each other and by the pipes. If you have any questions regarding Soft Water and Water Softeners please call the plumbers at Chambliss Plumbing Company at (210) 797-7471.
Choosing the right water softener system depends on your water source, hardness level, and household needs.
Grain Capacity and Sizing
Choosing the right water softener for your home means understanding grain capacity—the amount of hardness a unit can remove before it needs to regenerate. Grain capacity is measured in grains per week, and it’s important to match this to your household’s water usage and water hardness. To figure out how many grains your water softener should handle, start by multiplying your daily water usage by the water hardness (measured in grains per gallon). For example, if your household uses 225 gallons of water per day and your water hardness is 10 grains per gallon, you’ll need a water softener with a capacity of at least 2,250 grains per day.
A good rule of thumb is to estimate average water usage at 75 gallons per person per day. Multiply the number of people in your home by 75, then multiply that number by your water hardness in grains per gallon. This calculation will help you determine the right grain capacity for your water softener, ensuring it can keep up with your needs and deliver consistently soft water.
Water Softener Maintenance
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your water softener running smoothly and extending its lifespan, which typically ranges from 10 to 15 years. One of the most important tasks is checking the salt level in the brine tank every 4 to 6 weeks. If the salt runs low, your water softener won’t be able to produce soft water, and hard water will start flowing through your system again. It’s also important to inspect the brine tank for salt bridges, hardened layers of salt that can prevent the resin beads from regenerating properly. If you spot a salt bridge, break it up to restore normal operation.
Using the right type of water softener salt, such as cubes or crystal salt, is essential for optimal performance. Always refer to your owner’s manual to confirm which salt is best for your specific model. Additionally, periodically cleaning the resin bed with a water softener cleaner helps remove iron and other heavy metals from the resin beads, ensuring they can fully regenerate during the regeneration cycle. With these simple maintenance steps, you’ll enjoy high water quality and reliable softening for years to come.
Water Softener Installation
Installing a water softener can be a DIY project for those with plumbing experience, but many homeowners prefer professional installation to ensure everything is set up correctly. If you choose to install it yourself, start by shutting off your water supply and water heater, then drain the water lines. Connect the water softener to your existing plumbing using the appropriate 1-inch NPT fittings, and make sure all connections are secure. Fill the brine tank with the recommended water softener salt, check for leaks, and restart your water heater once installation is complete.
Before purchasing a water softener, measure the installation area and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications, as both salt based water softeners and salt free water softeners can require significant space. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take necessary safety precautions during installation. If you’re unsure about any step, or if your water softener system will be connected to other water-using appliances, it’s best to hire a professional to ensure your water softener operates safely and efficiently.
Drinking Water Quality
Softened water from a water softener is generally safe to drink, but it’s important to be aware of changes in mineral content. The World Health Organization notes that softened water contains less calcium and magnesium, so you may want to monitor your dietary intake of these essential minerals. Keep in mind that water softening does not remove harmful contaminants—any impurities present in your water supply before softening will remain afterward. To ensure your drinking water meets your standards, use a water test kit to measure water hardness and consider installing a water filter for added protection.
If you’re concerned about salt intake, salt free water softeners are an alternative that don’t add sodium to your water. However, salt free water softeners may not be as effective at removing hardness minerals as traditional salt based water softeners. Regularly testing your water quality and choosing the right water softening system for your needs will help you enjoy safe, great-tasting drinking water in your home.